Immunohistochemistry - Processing
- How the process works
- What components are used
- Direct or indirect
Immunohistochemistry or IHC refers to the process of detecting antigens in cells of a tissue section. This exploits the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues.
The most common instance, an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase, that can catalyse and make the area visible.
Picture 1 - IHC most common procedure
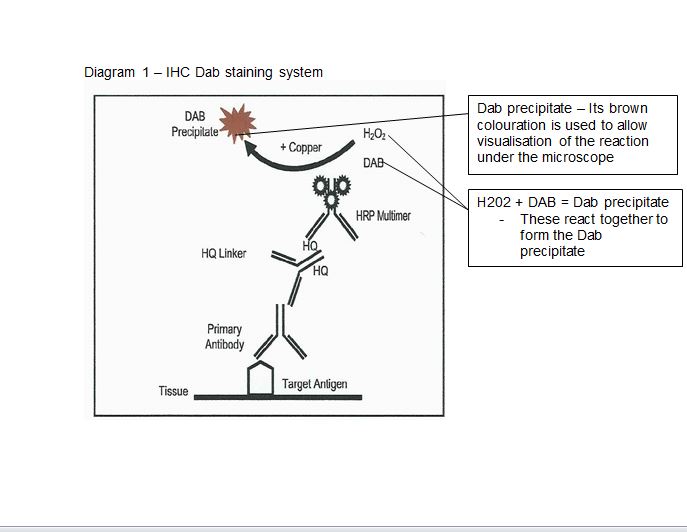
For this procedure several different components are required as shown in the table below for the IHC to be carried out.
Table 1 – Kit components for carrying out IHC
In the history of Immunohistochemistry there have been several different procedures. One of the biggest differences is whether to carry out a direct or indiret staining procedure as shown below.
Picture 1 – Direct and indirect differences
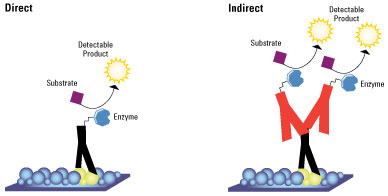
The techniques both have there advantages and disadvantages. The direct technique is less involved, has less background and is faster than the indirect. However most of the procedures carried out use the indirect technique. The reasons for this is that the indirect technique is more effective as signal amplification can be used. Also the other disadvantages have been worked on, using blocking agents to prevent contamination.
Overall the indirect technique has proven to be the most effective for use in large scale laboratories as well.
.